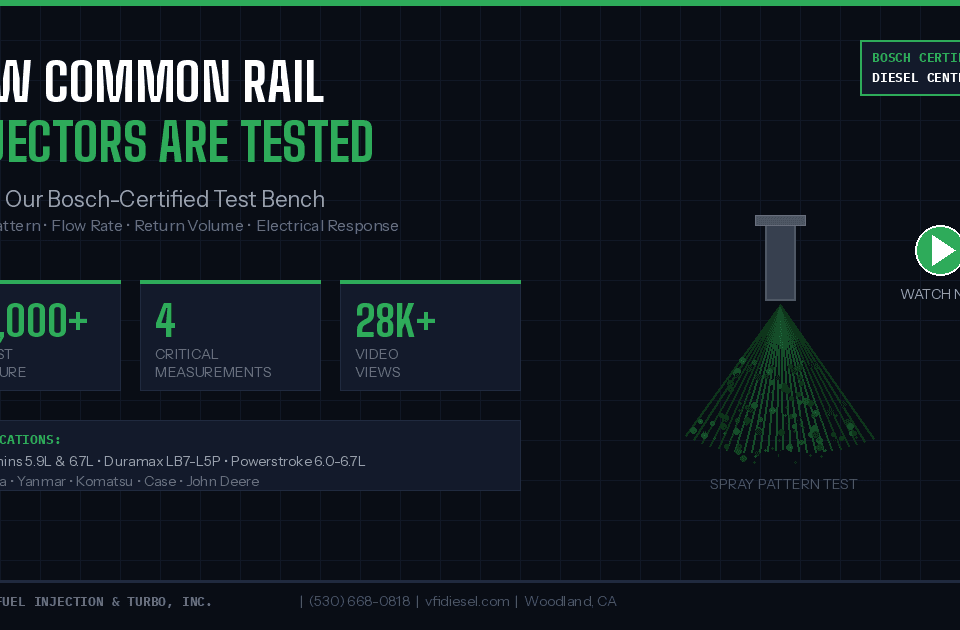
How Common Rail Diesel Injectors Are Tested: Inside Our Bosch-Certified Test Bench
22 February 2026
7 Diesel Injector Failure Symptoms: Warning Signs You Shouldn’t Ignore
22 February 2026Published by Valley Fuel Injection & Turbo, Inc. | Woodland, CA Reviewed by VFI’s Bosch-Certified Diesel Technicians
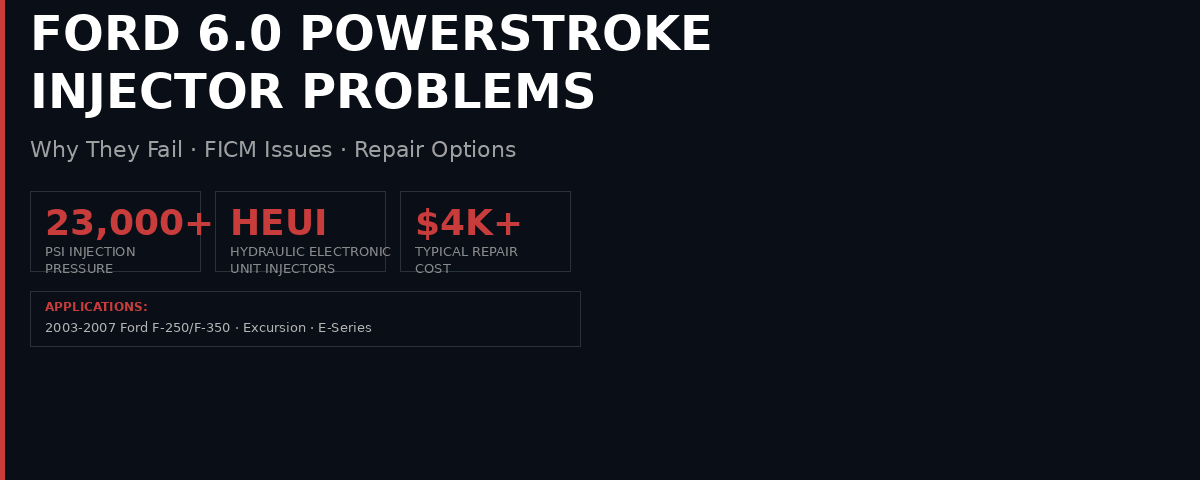
The Ford 6.0L Powerstroke diesel — found in 2003–2007 Ford F-250, F-350, F-450, F-550, Excursion, and E-Series vans — is one of the most notorious diesel engines when it comes to fuel injection problems. The 6.0 uses a Hydraulic Electronic Unit Injector (HEUI) system that’s powerful but complex, and when things go wrong, the repair bills stack up fast.
At Valley Fuel Injection & Turbo, we test and service 6.0 Powerstroke injectors on our Bosch-certified test bench every week. This guide covers why 6.0 injectors fail, how to diagnose problems, the role of the FICM, and your repair options.
How the 6.0 Powerstroke HEUI Injection System Works
Unlike conventional common rail diesels that use a high-pressure fuel pump to pressurize fuel directly, the 6.0 Powerstroke uses hydraulic pressure from the engine oil to fire the injectors. Here’s the chain:
- High-Pressure Oil Pump (HPOP) pressurizes engine oil to 500–3,600 PSI
- Injection Pressure Regulator (IPR) controls oil pressure to the injectors
- FICM (Fuel Injection Control Module) sends a 48-volt electrical signal telling each injector when and how long to fire
- HEUI Injectors use the high-pressure oil to multiply force and inject fuel at up to 23,000+ PSI into the combustion chamber
This system is elegant when it works. But it means there are three potential failure points for every injection event: oil pressure, electrical signal, and the injector itself. General diesel shops often misdiagnose 6.0 problems because they chase symptoms in one system when the actual failure is in another.
Common 6.0 Powerstroke Injector Failure Symptoms
If your 6.0 Powerstroke is showing any of these symptoms, injector problems should be high on your suspect list:
- Hard starting or long crank times — especially noticeable in cold weather. A failing injector can’t atomize fuel properly, making combustion difficult.
- Rough idle or engine miss — the engine shakes, stumbles, or feels like it’s running on fewer cylinders. This is often the first sign of injector trouble.
- White or blue exhaust smoke — unburned or partially burned fuel passing through the exhaust. Different from the black smoke you’d see with over-fueling.
- Loss of power under load — the truck feels sluggish on hills, when towing, or during acceleration. Injectors that can’t deliver the correct fuel quantity starve the engine.
- Excessive fuel in the oil (fuel dilution) — if your oil smells like diesel or the level is rising between changes, injectors are leaking fuel past internal seals into the crankcase. This is dangerous — diluted oil loses its lubricating properties and can cause catastrophic engine damage.
- High injector “buzz” test failure — a diagnostic buzz test uses the scan tool to fire each injector individually. Cylinders with contribution issues point directly to bad injectors.
- Diagnostic trouble codes: P0263, P0266, P0269, P0272, P0275, P0278, P0281, P0284 (cylinder contribution/balance codes), P0611 (FICM performance)
Why 6.0 Powerstroke Injectors Fail
1. Stiction (Internal Spool Valve Sticking)
The most common 6.0 injector problem. The internal spool valve that controls oil flow inside the injector develops a sticky buildup from oil deposits, especially in cold weather. The injector can’t respond quickly enough to the FICM signal, causing hard starts, rough idle, and misfires. Stiction is often worst on cold starts and improves as the engine warms up.
2. O-Ring Failure
Each 6.0 injector has multiple O-rings that seal oil pressure. When these fail, high-pressure oil leaks past the injector, causing loss of injection pressure and rough running. O-ring failure is extremely common on the 6.0 and can happen on trucks with relatively low mileage.
3. FICM Voltage Drop
The FICM needs to deliver a clean 48-volt signal to fire the injectors. When the FICM starts failing, voltage drops to 40V or lower, and injectors can’t fire properly. Symptoms mimic bad injectors — rough idle, misfires, white smoke — but the injectors themselves may be fine. Always check FICM voltage before condemning injectors. A scan tool should show 48V ± 1V. Anything below 45V is problematic.
4. High-Pressure Oil System Issues
Because the injectors rely on oil pressure to fire, any weakness in the high-pressure oil system affects injection. A failing HPOP, worn IPR, or leaking oil standpipes/dummy plugs can all cause symptoms that look like injector failure. If ICP (Injection Control Pressure) can’t reach or maintain target, the injectors can’t do their job regardless of their condition.
5. Contaminated or Low-Quality Oil
The 6.0 Powerstroke is extremely sensitive to oil quality because the same oil that lubricates the engine also fires the injectors. Extended oil change intervals, wrong oil viscosity, or contaminated oil accelerates stiction and spool valve wear. Running a quality 15W-40 diesel oil and changing it on time is critical for injector longevity on a 6.0.
Diagnosing 6.0 Powerstroke Injector Problems
Proper diagnosis of 6.0 injector problems requires a systematic approach because so many systems interact:
Step 1: Check FICM Voltage
Connect a scan tool and read FICM voltage. If it’s below 45V, the FICM needs to be addressed before touching injectors. Many trucks have had unnecessary injector replacements because the real problem was a $300 FICM repair, not a $3,500 injector set.
Step 2: Monitor ICP and IPR
Watch Injection Control Pressure (ICP) at idle and under load. Compare ICP desired vs. ICP actual. If the system can’t build or maintain pressure, look at the HPOP, IPR, standpipes, and dummy plugs before blaming injectors.
Step 3: Cylinder Contribution / Buzz Test
Use a scan tool to run an injector buzz test and check cylinder contribution. This identifies which specific cylinders are weak. But remember — a weak cylinder contribution could be the injector, or it could be low oil pressure to that injector bank.
Step 4: Bench Testing
The definitive answer. Remove the injectors and have them professionally bench tested on calibrated equipment. This measures actual flow rates, spray patterns, response time, and identifies exactly which injectors have failed. At Valley Fuel Injection, we test HEUI injectors on our Bosch-certified test bench and provide detailed results showing exactly what’s wrong.
6.0 Powerstroke Injector Repair Options
Option 1: Stiction Remedy / Oil Additive
For mild stiction symptoms (cold start rough idle that clears up when warm), a stiction eliminator oil additive can sometimes free sticky spool valves. This is a bandaid, not a fix — if stiction is severe, the injectors need to come out. Cost: $30–$60.
Option 2: Remanufactured Injectors
Professionally remanufactured HEUI injectors are rebuilt with new O-rings, spool valves, nozzles, and internal components, then tested to OEM specifications. This is the most cost-effective option for a reliable repair. Always replace all 8 injectors at once — the labor to access 6.0 injectors involves removing the valve covers and high-pressure oil rails, so you don’t want to do it twice. Cost: $2,500–$4,500 for a full set with labor.
Option 3: New OEM Injectors
Brand new injectors from the dealer. Most expensive option but comes with a factory warranty. Cost: $4,000–$6,000+ for all 8 with labor.
How Much Does 6.0 Powerstroke Injector Replacement Cost?
Total cost depends on whether you’re doing a partial or complete repair:
- Injector bench testing: $30–$75 per injector
- Full set remanufactured injectors (8): $1,800–$3,000 for parts
- Full set new OEM injectors (8): $3,000–$4,500 for parts
- Labor for replacement: $800–$1,500 (6–10 hours)
- FICM repair/replacement: $200–$800 if needed
- Standpipes, dummy plugs, O-rings: $100–$300 for the kit
Total typical cost: $3,000–$5,500 for a complete injector replacement with all supporting hardware. Getting a proper diagnosis first can save you from replacing parts that don’t need replacing.
Preventing 6.0 Powerstroke Injector Problems
- Change oil religiously — every 5,000 miles with a quality 15W-40 diesel oil. The 6.0 is not forgiving of extended intervals.
- Use quality fuel filters — change the fuel filter every 10,000–15,000 miles. Water contamination destroys injector internals.
- Drain the fuel/water separator — check and drain regularly, especially in humid climates.
- Let the engine warm up — don’t hammer a cold 6.0. Let oil pressure build and the FICM voltage stabilize before putting it under load.
- Monitor FICM voltage — check periodically with a scan tool. Catching a FICM voltage drop early prevents injector damage from improper firing signals.
- Consider a coolant filter — the 6.0’s EGR cooler failures can push coolant into the oil system, contaminating injection oil. A coolant filter adds protection.
Why Choose Valley Fuel Injection for 6.0 Powerstroke Service?
The 6.0 Powerstroke’s HEUI system requires specialized knowledge that most general shops don’t have. At Valley Fuel Injection, we’ve been testing and servicing diesel injectors — including HEUI units — for over 30 years. Our Bosch-certified facility in Woodland, CA has the calibrated test equipment to properly diagnose whether your problem is injectors, FICM, oil pressure, or a combination.
We serve 6.0 Powerstroke owners from Sacramento, Roseville, Stockton, Reno, and across Northern California. We also offer mail-in injector testing — pull your injectors (or have your local shop do it), ship them to us, and we’ll bench test them and report back exactly what’s needed.
Dealing with 6.0 Powerstroke injector problems?
Don’t guess — get a proper diagnosis. Call (530) 668-0818 or contact us online for 6.0 Powerstroke injector testing and repair.
Valley Fuel Injection & Turbo, Inc.
1243 E Beamer St, Suite C, Woodland, CA 95776
Monday–Friday, 7:00 AM – 4:30 PM PST
Related reading: VP44 Injection Pump Failure Guide · LB7 Duramax Injector Replacement · 6.7 Cummins Injector Problems · How Injectors Are Tested